Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
Pancreatic cancer is a serious disease that starts in the pancreas, a small organ behind your stomach that helps with digestion and blood sugar control. Though it is a challenging condition, understanding it better can help in early detection and treatment.
What Is the Pancreas and Why Is It Important?
The pancreas is about 6 inches long and shaped like a flat pear. It has two main jobs:
- Digestive Enzymes: It produces enzymes that break down food so your body can absorb nutrients.
- Hormones: It makes insulin and other hormones to regulate your blood sugar levels.
What Is Pancreatic Cancer?

Pancreatic cancer occurs when cells in the pancreas grow uncontrollably. These abnormal cells can form tumors and spread to other parts of the body. The disease is often discovered late because the pancreas is located deep inside the body, and symptoms may not appear until it’s advanced.
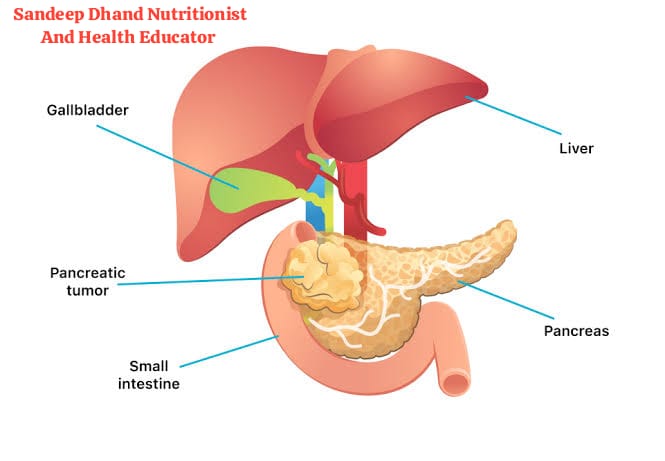
Types of Pancreatic Cancer
There are two main types of pancreatic cancer:
- Exocrine Pancreatic Cancer:
This is the most common type and starts in the ducts that carry digestive enzymes.
Example: Adenocarcinoma.
- Endocrine Pancreatic Cancer:
This is rare and starts in the hormone-producing cells of the pancreas.
Example: Neuroendocrine tumors.
What Causes Pancreatic Cancer?
The exact cause of pancreatic cancer is unclear, but certain risk factors increase your chances of developing it.
Who Is at Risk?
Several factors can make someone more likely to get pancreatic cancer:
- Lifestyle Factors:
Smoking: Smokers are twice as likely to develop this cancer.
Obesity: Excess body weight puts pressure on the pancreas.
- Medical History:
Diabetes: Long-standing diabetes can increase the risk.
Chronic Pancreatitis: Long-term inflammation of the pancreas.
- Family History:
If your parents or siblings have had pancreatic cancer, your risk increases.
- Age and Gender:
People over 60 are at higher risk, and men are slightly more likely to develop it.
What Are the Symptoms?
The symptoms of pancreatic cancer often appear late, which is why it’s hard to catch early. Common signs include:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, often with dark urine and pale stools.
- Abdominal or Back Pain: A dull ache that worsens over time.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained and sudden weight loss is common.
- Loss of Appetite: Feeling full quickly or not wanting to eat.
- Fatigue: Constant tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Digestive Issues: Nausea, vomiting, or difficulty digesting fatty foods.
How Is Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosed?
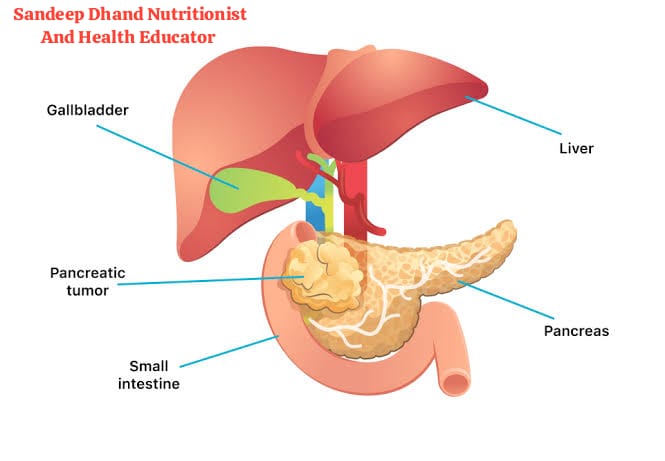
Doctors use several tools to confirm if someone has pancreatic cancer:
- Imaging Tests:
CT Scan: Provides detailed pictures of the pancreas.
MRI: Helps spot tumors in soft tissues.
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): Uses sound waves to get a close look at the pancreas.
- Blood Tests:
Tests like CA 19-9 measure specific markers linked to pancreatic cancer.
- Biopsy:
A small tissue sample is taken from the pancreas to check for cancer cells.
Stages of Pancreatic Cancer
Cancer is categorized into stages based on how far it has spread:
- Stage 1: Cancer is only in the pancreas.
- Stage 2: It has grown into nearby tissues but not major blood vessels.
- Stage 3: Cancer has spread to nearby blood vessels or lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: It has spread to distant organs like the liver or lungs.
How Is Pancreatic Cancer Treated?
Treatment depends on the stage of cancer and the patient’s overall health.
- Surgery:
If detected early, surgery can remove the tumor.
Common procedure: Whipple Surgery, which removes part of the pancreas, small intestine, and nearby tissues.
- Chemotherapy:
Uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
Often combined with radiation or surgery.
- Radiation Therapy:
High-energy rays target and kill cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy:
Focuses on specific molecules in cancer cells, causing less harm to normal cells.
- Immunotherapy:
Boosts the immune system to attack cancer cells.
Challenges in Treatment
Pancreatic cancer is hard to treat for several reasons:
It is often diagnosed late.
It spreads quickly to other parts of the body.
Tumors in the pancreas can be resistant to standard treatments.
How to Reduce the Risk of Pancreatic Cancer
While you can’t control all risk factors, certain lifestyle changes can help:
- Quit Smoking:
Smoking is one of the biggest risk factors.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Regular exercise and a balanced diet can reduce the risk.
- Control Diabetes:
Proper management of blood sugar levels is essential.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive alcohol can lead to pancreatitis, increasing the risk.
- Eat a Healthy Diet:
Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limit processed foods.
Living With Pancreatic Cancer
If diagnosed, managing pancreatic cancer involves medical treatment and emotional support:
- Medical Care:
Follow your doctor’s advice and attend regular check-ups.
- Emotional Support:
Seek support from family, friends, or counseling groups.
- Dietary Adjustments:
A dietitian can help with meal planning to manage symptoms like nausea or weight loss.
- Pain Management:
Pain-relieving medications or therapies can improve quality of life.
Outlook and Survival Rates
Pancreatic cancer has a lower survival rate compared to other cancers, mainly due to late detection. However, early diagnosis and advancements in treatment are improving outcomes.
Why Early Detection Matters
Identifying pancreatic cancer early can make a big difference. Be proactive about your health:
See a doctor if you have persistent symptoms.
Discuss your family history with your doctor.
Hope Through Research
Ongoing research is focused on finding better ways to detect and treat pancreatic cancer. Clinical trials are exploring new drugs, therapies, and early detection methods.
Conclusion
Pancreatic cancer is a challenging disease, but understanding it can lead to better prevention, earlier diagnosis, and improved treatment options. Staying informed and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can make a significant difference. If you or a loved one is affected, don’t hesitate to seek medical help and support.
By staying vigilant and supporting research efforts, we can hope for better outcomes in the fight against pancreatic cancer.
