Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
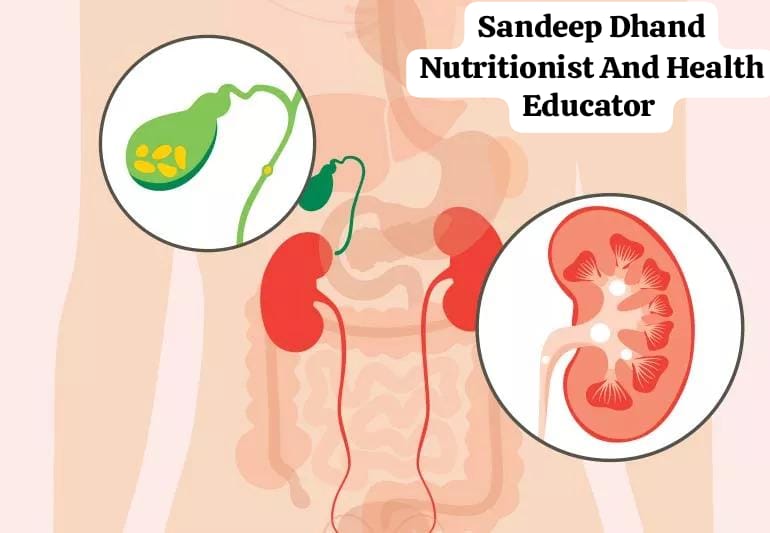
The human body is a complex system where even minor imbalances can lead to significant health issues. Two common but painful conditions that many people face are gallstones and kidney stones. Although they affect different organs, their formation, causes, and symptoms can often confuse people. This article explores these conditions in depth, using simple language to help you understand how they develop, what causes them, and how you can prevent them.
What Are Gallstones?
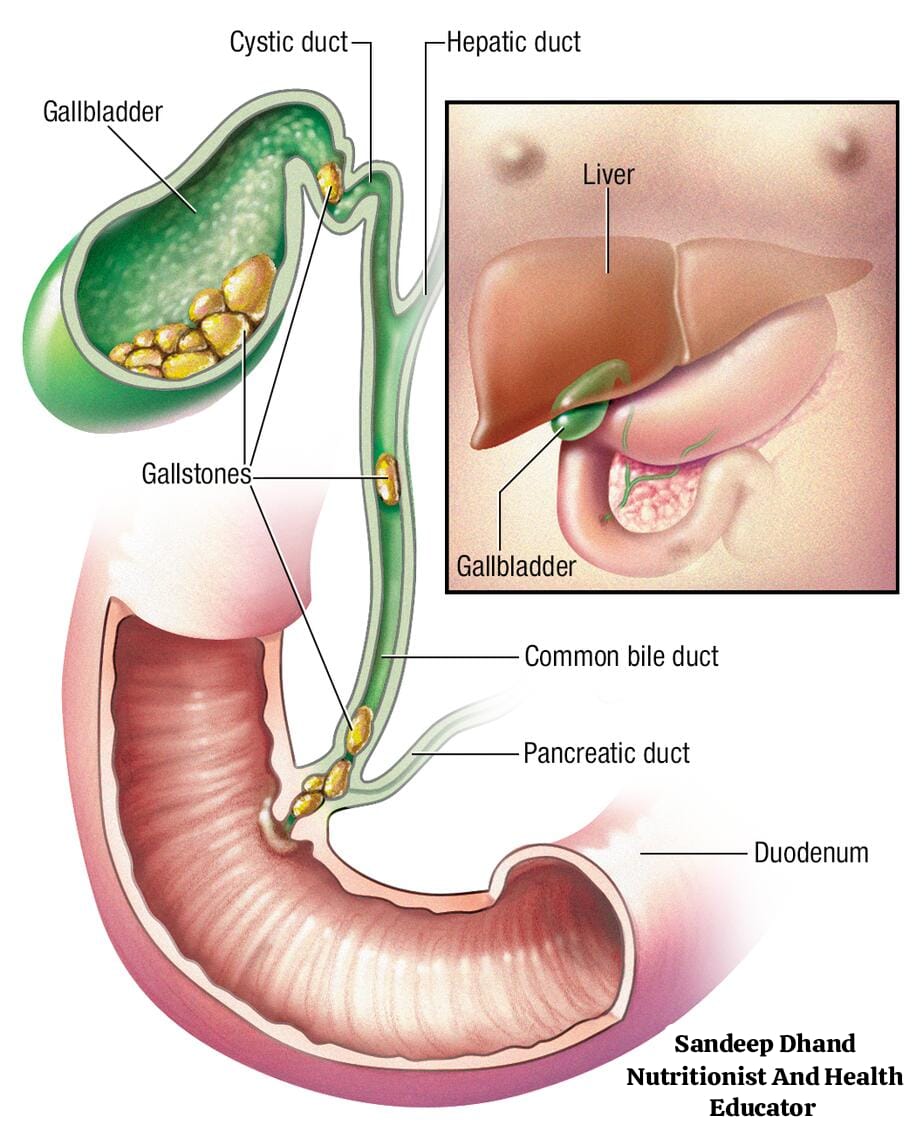
Gallstones are small, hard particles that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver. The gallbladder stores and releases bile, a digestive fluid that helps break down fats. Gallstones can range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball.
How Do Gallstones Form?
Gallstones form when the bile in your gallbladder becomes imbalanced. This can happen in the following ways:
- Excess Cholesterol in Bile: When your bile contains too much cholesterol, it can form crystals that grow into stones.
- High Bilirubin Levels: Bilirubin is a substance produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. High levels can lead to stone formation.
- Poor Bile Flow: If the gallbladder does not empty properly, bile can become concentrated and form stones.
Who Is at Risk of Gallstones?
Some factors that increase the risk of gallstones include:
Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to high cholesterol levels in bile.
Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in fats and sugars can contribute to gallstone formation.
Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly can disturb the balance of bile.
Family History: If your family members have had gallstones, your chances are higher.
Age and Gender: Women, especially those over 40, are more likely to develop gallstones due to hormonal changes.
Symptoms of Gallstones

Gallstones may not always cause symptoms. When they do, the most common signs include:
Sudden, intense pain in the upper right abdomen.
Nausea or vomiting.
Pain in the right shoulder or back.
Digestive issues, such as bloating or indigestion.
How Are Gallstones Treated?
- Medications: Some medicines can dissolve small gallstones, though they are not always effective.
- Surgery: If gallstones cause severe symptoms, doctors may recommend removing the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
- Lifestyle Changes: Eating a healthy diet and maintaining a balanced weight can help manage gallstones.
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. The kidneys filter waste and excess substances from your blood, which are excreted as urine. When urine contains too many minerals, they can crystallize and stick together, forming stones.
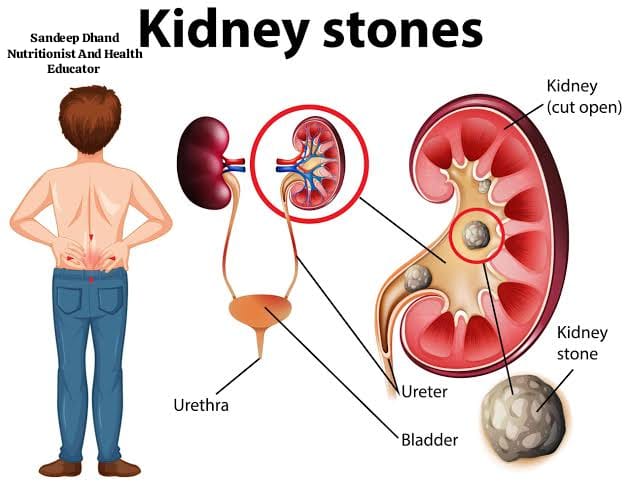
How Do Kidney Stones Form?
Kidney stones form when your urine becomes too concentrated. This can happen due to:
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water increases the concentration of minerals in your urine.
- High Calcium Levels: Excess calcium can combine with oxalate or phosphate to form stones.
- High Uric Acid Levels: A diet rich in red meat and seafood can lead to elevated uric acid, which can form stones.
- Imbalance in Urine pH: Urine that is too acidic or too alkaline can promote stone formation.
Types of Kidney Stones
There are different types of kidney stones based on their composition:
- Calcium Stones: The most common type, formed from calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate.
- Uric Acid Stones: Common in people who consume a lot of animal protein.
- Struvite Stones: Usually caused by urinary tract infections.
- Cystine Stones: Rare and caused by a genetic disorder.
Who Is at Risk of Kidney Stones?
Risk factors for kidney stones include:
Dehydration: Drinking less water increases the risk.
Diet: Consuming a diet high in salt, sugar, and animal protein can contribute to stone formation.
Family History: If kidney stones run in your family, your risk is higher.
Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like gout and inflammatory bowel disease increase the risk.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
The symptoms of kidney stones depend on their size and location. Common signs include:
Severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen.
Pain while urinating.
Blood in the urine (pink, red, or brown urine).
Frequent urge to urinate.
Nausea and vomiting.
How Are Kidney Stones Treated?
- Medications: Pain relievers and drugs that relax the ureter can help pass stones.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out smaller stones.
- Shock Wave Therapy: High-energy sound waves break stones into smaller pieces.
- Surgery: Larger stones may require surgical removal.
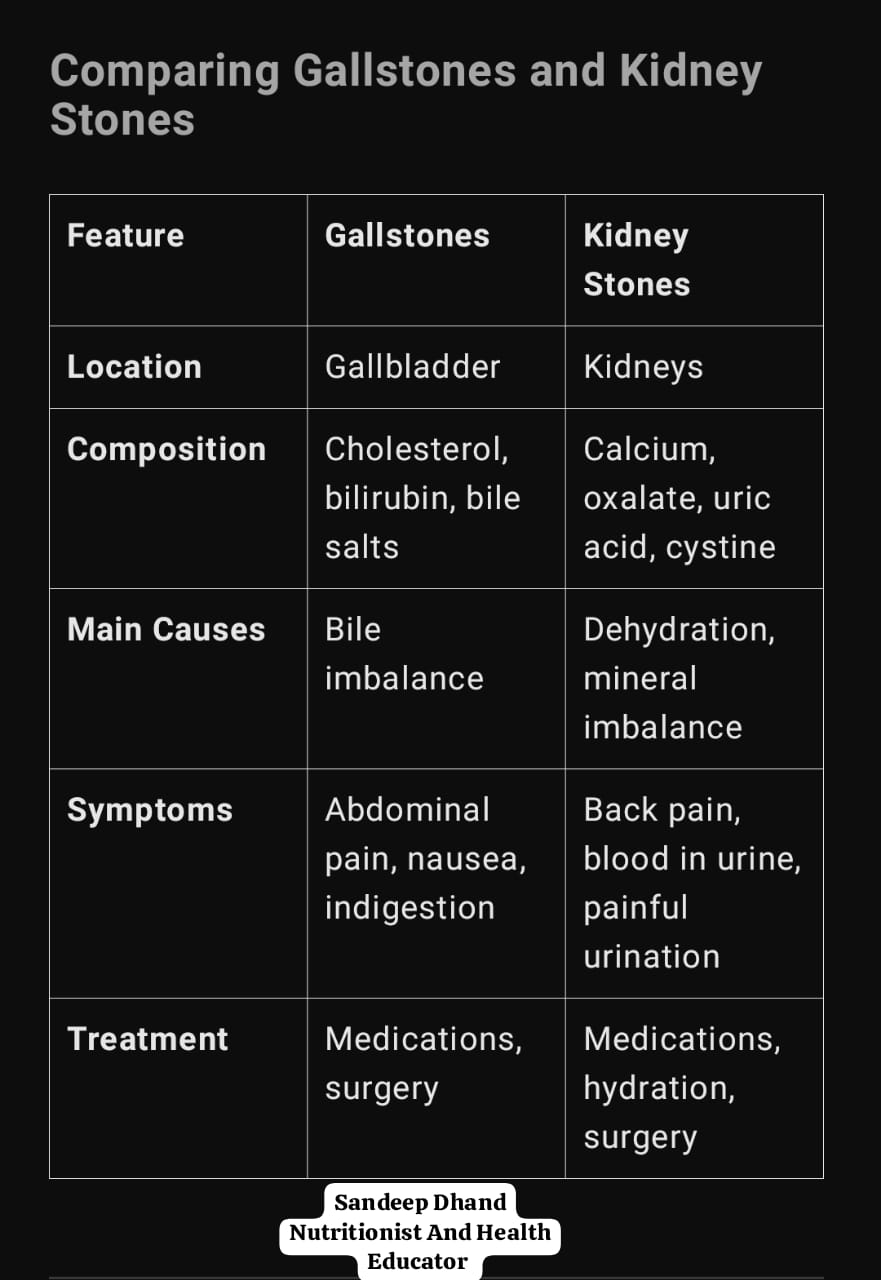
Comparing Gallstones and Kidney Stones
Preventing Gallstones and Kidney Stones
While some risk factors like genetics cannot be controlled, you can take steps to reduce your chances of developing gallstones and kidney stones.
Prevention Tips for Gallstones
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid crash diets or rapid weight loss.
- Eat a balanced diet with plenty of fiber and low-fat foods.
- Stay active to improve digestion and bile flow.
Prevention Tips for Kidney Stones
- Drink plenty of water (8-10 glasses daily).
- Limit salt, sugar, and animal protein intake.
- Include citrus fruits like lemons and oranges in your diet to prevent stone formation.
- Monitor your calcium intake to avoid excessive consumption.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
Persistent or severe pain in the abdomen or back.
Blood in your urine.
High fever or chills along with other symptoms.
Difficulty passing urine or changes in urine color.
Conclusion
Gallstones and kidney stones can cause significant discomfort and may lead to complications if left untreated. Understanding how they form, the factors that increase their risk, and ways to prevent them is essential for maintaining good health. Simple lifestyle changes, such as staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and avoiding unhealthy habits, can go a long way in reducing your risk. If you suspect you have gallstones or kidney stones, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Your health is in your hands, and small steps today can prevent big problems tomorrow.