Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
Alzheimer’s disease is a condition that affects the brain, making it hard for people to remember things, think clearly, or carry out everyday tasks. It is the most common cause of dementia, a term used to describe problems with memory and thinking that get worse over time. Let’s explore this condition in simple terms to understand what it is, how it happens, and how it affects people.
What Happens in Alzheimer’s Disease?
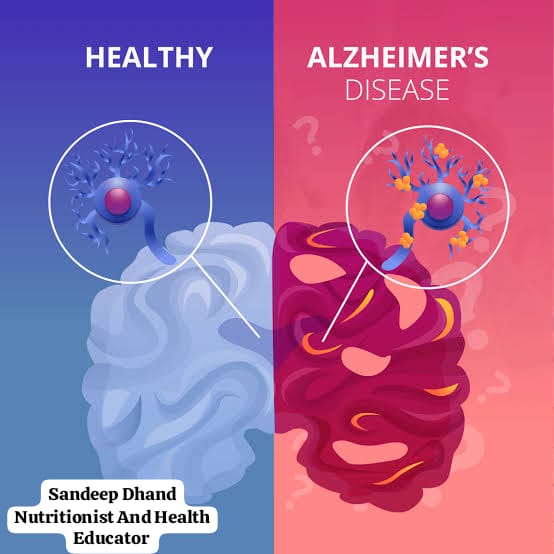
Our brain is like a control center that helps us think, remember, and do daily activities. In Alzheimer’s disease, certain parts of the brain stop working properly. This happens because:
Plaques and Tangles: Harmful proteins called amyloid plaques and tau tangles build up in the brain. These block communication between brain cells and cause them to die.
Brain Shrinkage: Over time, the brain becomes smaller because many cells are damaged or lost.
Why Do People Get Alzheimer’s?
Doctors don’t know exactly what causes Alzheimer’s, but there are things that increase the risk:
- Age: It mostly affects people over 65, though younger people can also get it (this is called early-onset Alzheimer’s).
- Family History: If someone in your family had Alzheimer’s, you might have a higher chance of getting it.
- Lifestyle: Unhealthy habits like smoking, poor diet, and not exercising can increase the risk.
- Health Problems: Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease may also play a role.
What Are the Symptoms?
Alzheimer’s usually starts with mild problems and gets worse over time. Common signs include:
Memory Loss: Forgetting recent events, names, or conversations.
Confusion: Not knowing the time, date, or where you are.
Difficulty Solving Problems: Trouble with tasks like paying bills or following a recipe.
Mood Changes: Feeling anxious, confused, or upset more often.
Trouble Communicating: Struggling to find the right words or complete sentences.
Stages of Alzheimer’s

Alzheimer’s progresses in stages, starting with mild symptoms and gradually worsening:
- Early Stage: People might forget small things, like where they put their keys or a recent conversation. They can still live independently but may need reminders.
- Middle Stage: Memory problems and confusion become more noticeable. People may forget family members’ names, have trouble dressing, or get lost in familiar places.
- Late Stage: In this stage, individuals often need full-time care. They may lose the ability to speak, recognize loved ones, or take care of themselves.
How Is Alzheimer’s Diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose Alzheimer’s, such as:
Asking about symptoms and family history.
Conducting memory and thinking tests.
Doing brain scans like MRI or CT to check for changes in the brain.
Can Alzheimer’s Be Cured?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s. However, there are treatments that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Medications: Some drugs can temporarily improve memory or reduce symptoms like confusion.
- Lifestyle Changes: Eating healthy, exercising, and staying mentally active can help slow the progression.
- Therapies: Activities like puzzles, music, or art therapy can help patients stay engaged and happy.
How Can You Help Someone with Alzheimer’s?
Caring for someone with Alzheimer’s can be challenging, but patience and understanding can make a big difference. Here are some tips:
Be Supportive: Gently remind them of things they forget and help them with daily tasks.
Create a Safe Space: Make their home safe by removing tripping hazards and keeping things they need within easy reach.
Stay Calm: If they get confused or upset, stay calm and reassure them.
Engage Them: Encourage activities they enjoy, like listening to music, gardening, or simple crafts.
Can Alzheimer’s Be Prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent Alzheimer’s, certain habits can lower the risk:
Stay Active: Exercise regularly to keep your brain and body healthy.
Eat Healthy: Follow a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
Challenge Your Mind: Read, solve puzzles, or learn something new to keep your brain sharp.
Socialize: Spend time with friends and family to stay mentally and emotionally connected.
In Conclusion
Alzheimer’s disease is a heartbreaking condition that affects not just the person diagnosed but also their loved ones. While there is no cure, understanding the disease and providing care with love and patience can make life a little easier for everyone involved. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, we can reduce the risk and support ongoing research to find better treatments in the future.