Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
The parotid gland is one of the largest salivary glands in the human body. Salivary glands are essential for the production and secretion of saliva, which plays a critical role in digestion, oral hygiene, and overall health. Located on either side of the face, just in front of and below the ears, the parotid glands are responsible for secreting a significant portion of saliva into the mouth. This saliva contains enzymes like amylase that help break down carbohydrates during the initial stages of digestion.
Anatomy of the Parotid Gland
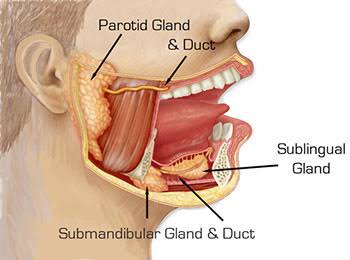
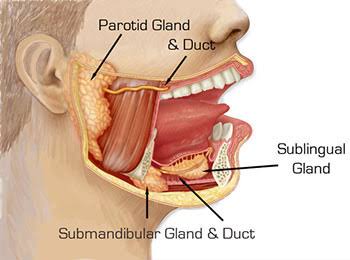
Each parotid gland is shaped like an inverted pyramid and is encased in a fibrous capsule. It is divided into two parts:
- Superficial lobe: Lies just beneath the skin and is the more visible part of the gland.
- Deep lobe: Located deeper within the tissue, extending towards the pharynx.
The facial nerve, which controls the muscles of facial expression, passes through the parotid gland. However, the nerve does not control the gland’s secretion function; this is managed by autonomic nervous system signals.
The gland’s saliva is transported to the mouth via the Stensen’s duct, which opens near the upper second molar.
Functions of the Parotid Gland
- Saliva Production: Produces serous, watery saliva rich in enzymes.
- Digestive Role: Saliva aids in breaking down starches into simpler sugars through amylase.
- Lubrication: Saliva keeps the oral cavity moist, aiding in speech and swallowing.
- Protection: Saliva has antimicrobial properties that help protect against infections.
Common Parotid Gland Disorders
Various conditions can affect the parotid gland, ranging from infections to tumors. Here are some common issues:
- Parotitis:
Inflammation of the parotid gland, often caused by infections such as mumps (a viral infection) or bacterial infections. - Sialolithiasis (Salivary Stones):
The formation of stones in the salivary ducts can block the flow of saliva, causing pain and swelling. - Tumors:
Parotid tumors can be benign (like pleomorphic adenomas) or malignant (like mucoepidermoid carcinoma). Symptoms may include a lump near the gland, facial nerve weakness, or pain. - Sjogren’s Syndrome:
An autoimmune disorder where the body attacks its own salivary glands, leading to dry mouth and swelling. - Trauma:
Physical injury to the parotid region can lead to gland dysfunction. - Chronic Parotitis:
Recurrent inflammation, sometimes without an obvious infection, often due to ductal obstructions or autoimmune conditions.
Symptoms of Parotid Gland Disorders
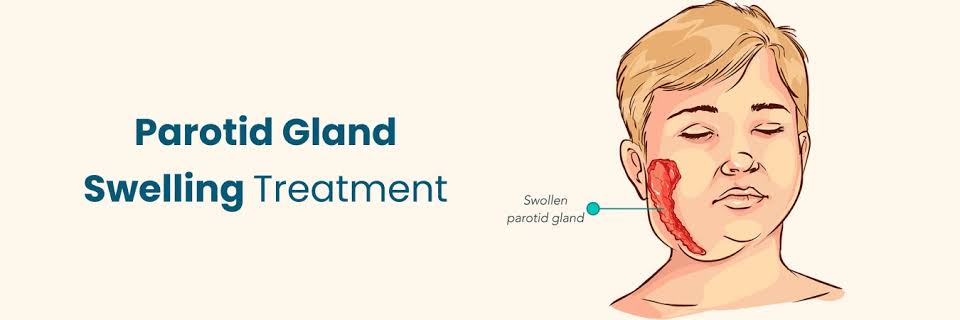
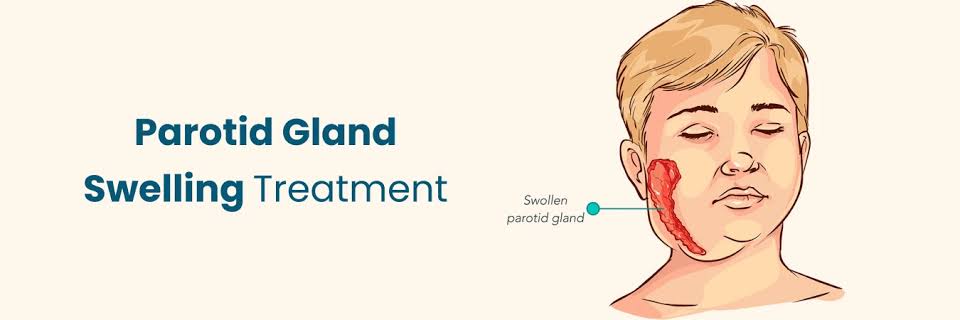
Swelling near the jawline or under the ear
Pain or tenderness in the gland
Dry mouth or reduced saliva production
Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
Pus discharge into the mouth (in cases of bacterial infection)
Fever and fatigue (if infection is present)
Facial nerve weakness or paralysis (in severe cases)
Diagnosis of Parotid Gland Issues
If you suspect a problem with your parotid gland, medical evaluation is essential. Common diagnostic methods include:
- Physical Examination: To check for swelling, tenderness, or lumps.
- Imaging Tests:
Ultrasound
CT scan or MRI
Sialography (X-ray of salivary ducts)
- Biopsy: To determine the nature of a tumor.
- Blood Tests: May reveal signs of infection or autoimmune disorders.
Prevention and Management of Parotid Gland Problems
While some conditions affecting the parotid gland are unavoidable, others can be prevented or managed with proper care.
Prevention Tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake helps maintain saliva flow, reducing the risk of blockages and infections.
- Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss regularly to prevent bacterial buildup in the mouth.
- Avoid Tobacco and Alcohol: Both can irritate salivary glands and increase the risk of tumors.
- Balanced Diet: Include foods rich in antioxidants and vitamins to support overall gland health.
- Regular Checkups: Routine dental and medical visits can help detect issues early.
Treatment Options:
- Infections:
Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
Rest and hydration for viral infections like mumps.
- Salivary Stones:
Massaging the gland and warm compresses may help dislodge small stones.
Larger stones might require removal through surgery or endoscopy.
- Tumors:
Surgery is the primary treatment for both benign and malignant tumors. Radiation or chemotherapy may be necessary for cancerous growths.
- Autoimmune Disorders:
Medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
- Chronic Conditions:
Lifestyle changes, hydration, and sometimes surgical interventions.
Home Remedies and Natural Care
For mild symptoms, you can try these remedies:
Warm Compress: Helps reduce swelling and pain.
Lemon Drops: Stimulate saliva production if the gland is not functioning optimally.
Good Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to keep the glands working efficiently.
Saltwater Rinse: Useful for oral hygiene and infection prevention.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you experience:
Persistent swelling or lumps near the ear or jaw
Severe pain that doesn’t improve
Dry mouth lasting for several days
Fever, pus discharge, or facial nerve weakness
Conclusion
The parotid gland plays an essential role in oral health and digestion. While it usually functions seamlessly, it can sometimes develop issues ranging from minor infections to severe tumors. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining oral hygiene, and seeking timely medical care can help prevent and manage parotid gland disorders effectively. If you notice any unusual symptoms, consult a healthcare provider promptly to ensure early diagnosis and treatment.