Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
Introduction
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common virus that usually causes mild respiratory infections. While most people recover without complications, it can lead to severe illness in young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems. This article explains everything about HMPV in a simple, easy-to-understand manner, covering symptoms, causes, prevention, and treatment.
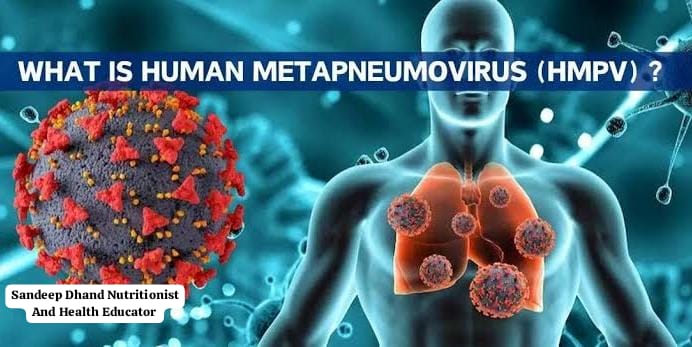
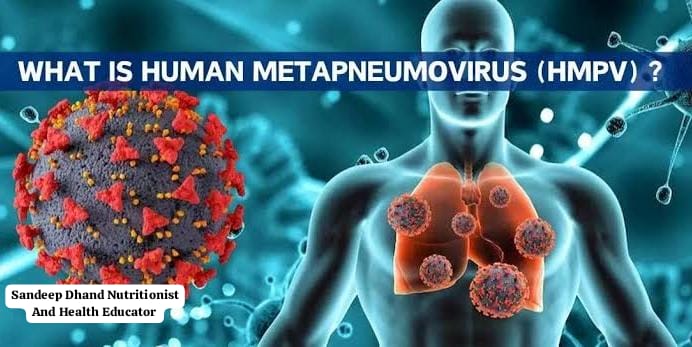
What is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
HMPV is a virus that primarily affects the respiratory system. It belongs to the same family as the viruses that cause RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus), measles, and mumps. While it often causes mild symptoms similar to the common cold, it can sometimes lead to more severe respiratory conditions like pneumonia or bronchitis.
Symptoms of HMPV
Most people with HMPV experience symptoms that are similar to a cold. These include:
Cough: Often dry or persistent.
Runny or Stuffy Nose: A typical sign of a respiratory infection.
Sore Throat: Caused by irritation from coughing.
Fever: Generally mild but can be higher in severe cases.
Shortness of Breath: In severe infections.
Wheezing: Common in young children or those with asthma.
In rare cases, a rash or ear infections may also occur.
How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV spreads from person to person through:
- Coughing and Sneezing: Virus-filled droplets can travel through the air.
- Direct Contact: Shaking hands, hugging, or kissing someone infected.
- Touching Contaminated Surfaces: Objects like door handles, toys, or phones can harbor the virus.
It is more common in the winter and early spring, similar to other respiratory viruses.

Who is at Risk?
While anyone can get HMPV, certain groups are more likely to experience severe illness:
Children under 5 years old: Especially premature infants.
Adults over 65 years old: Due to weaker immune systems.
People with chronic illnesses: Such as asthma or COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease).
Immunocompromised individuals: Those with conditions like HIV, cancer, or autoimmune diseases.
Complications of HMPV
In some cases, HMPV can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the airways.
- Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs.
- Asthma Flare-Ups: Triggered by respiratory infections.
- Ear Infections: Especially in young children.
- Bronchiolitis: Common in infants and young children.
Severe cases may require hospitalization, particularly for those in high-risk groups.
Diagnosis of HMPV
Doctors usually diagnose HMPV based on symptoms and medical history. In more severe cases, specific tests may be conducted:
- Nasal or Throat Swab: A sample is collected to identify the virus.
- Chest X-rays: To check for pneumonia or other lung conditions.
- Bronchoscopy: Rarely used but helps examine the airways.
Most people don’t need specialized tests unless their symptoms are severe.
How is HMPV Treated?
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for HMPV. Most people recover on their own with supportive care, which includes:
- Rest: Allow your body to recover.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Use pain relievers, decongestants, or cough suppressants to manage symptoms.
For severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary, and treatments could include:
Oxygen Therapy: For those with difficulty breathing.
IV Fluids: To maintain hydration.
Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation.
Antibiotics are not effective against HMPV because it is a virus, not a bacterial infection.
How Long Does HMPV Last?
Mild cases usually resolve within 7-10 days. However, severe cases may take longer to recover, especially if complications like pneumonia occur. Lingering symptoms, such as a persistent cough, may last for weeks.
Preventing HMPV
While it’s impossible to completely avoid HMPV, you can reduce your risk by following these simple precautions:
- Wash Your Hands Frequently: Use soap and water or hand sanitizer.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Especially your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Cover Your Coughs and Sneezes: Use a tissue or your elbow.
- Clean and Disinfect Surfaces: Especially commonly touched objects.
- Avoid Close Contact: Stay away from people who are sick.
Wearing a mask in crowded places can also reduce the risk of spreading or catching respiratory infections.
Is HMPV the Same as RSV?
No, HMPV and RSV are not the same, but they are similar. Both belong to the Pneumovirus genus and cause respiratory infections. However:
HMPV is more likely to cause severe illness in children aged 6-12 months.
RSV is more dangerous for infants younger than 6 months.
Both viruses can lead to complications in high-risk groups.
Taking Care of Yourself at Home
If you or your child has HMPV, you can manage the symptoms at home by:
- Resting as Much as Possible: To conserve energy.
- Using a Humidifier: To ease breathing.
- Staying Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids like water, soup, or herbal tea.
- Avoiding Smoke or Irritants: These can worsen symptoms.
Always consult a healthcare provider before giving over-the-counter medications to young children.
When to See a Doctor
You should contact a healthcare provider if:
Symptoms last longer than a week.
Fever persists for more than three days.
Symptoms worsen, or new symptoms appear.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Go to the ER immediately if:
You or your child has difficulty breathing.
There is a bluish tint to the skin, lips, or nails.
There is a high fever (above 103°F or 40°C).
Common Questions About HMPV
- How is HMPV different from a common cold?
HMPV often causes cold-like symptoms, but it can lead to serious respiratory conditions, especially in high-risk groups.
- Can I get HMPV more than once?
Yes, you can get HMPV multiple times, but symptoms are usually milder after the first infection.
- Is there a vaccine for HMPV?
Currently, there is no vaccine for HMPV, but research is ongoing.
Outlook for HMPV
Most people recover fully from HMPV within a week. However, for high-risk individuals, complications can occur, and medical intervention may be required. Early detection and proper care can significantly improve outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a common virus that usually causes mild illness. However, it can become serious for certain groups, including young children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems. By following preventive measures and seeking medical care when needed, you can reduce the risks associated with HMPV.
If you or a loved one experiences severe symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek medical help. Understanding this virus and taking precautions can go a long way in staying healthy.
