Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
Alcohol consumption has been a topic of debate for decades. While moderate drinking is often considered a social norm and even linked to some health benefits, the risks associated with excessive or prolonged alcohol use are significant. One of the most concerning risks is its potential to cause cancer. In this article, we will explore the relationship between alcohol consumption and cancer in simple terms, helping you understand why moderation is key and what the science says about this link.

Understanding Alcohol and Its Effects on the Body
Alcohol, or ethanol, is a chemical compound found in beverages like beer, wine, and spirits. When consumed, it is absorbed into the bloodstream and metabolized by the liver. Small amounts of alcohol are generally processed efficiently by the body. However, regular and heavy drinking can strain the liver, damage cells, and lead to long-term health problems.
One of the key issues with alcohol is its conversion into a toxic substance called acetaldehyde during metabolism. Acetaldehyde can damage DNA and prevent the body from repairing it effectively, leading to mutations that increase the risk of cancer.
Types of Cancers Linked to Alcohol
Scientific research has established a strong link between alcohol consumption and several types of cancer. Here are the most common ones:
- Mouth and Throat Cancer

Alcohol irritates the lining of the mouth and throat, making cells more vulnerable to damage. Regular drinking, especially when combined with smoking, significantly increases the risk of oral and throat cancers.
- Esophageal Cancer
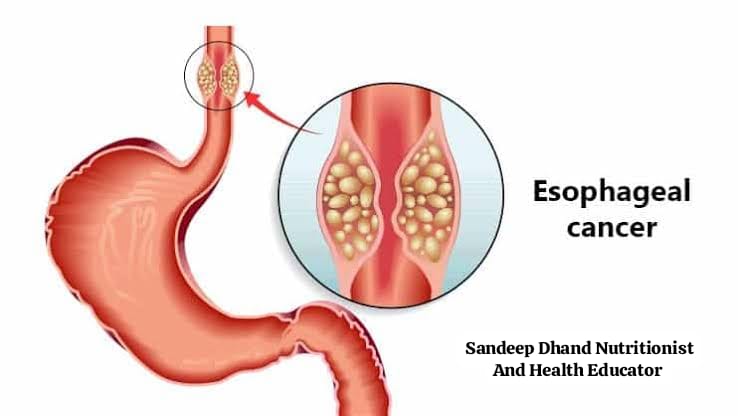
The esophagus, which carries food from the throat to the stomach, is highly susceptible to alcohol-induced damage. A particular genetic mutation that affects alcohol metabolism can further increase the risk of esophageal cancer in some people.
- Breast Cancer
Even moderate alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of breast cancer in women. Alcohol can raise estrogen levels, a hormone that promotes the growth of breast cancer cells.
- Liver Cancer
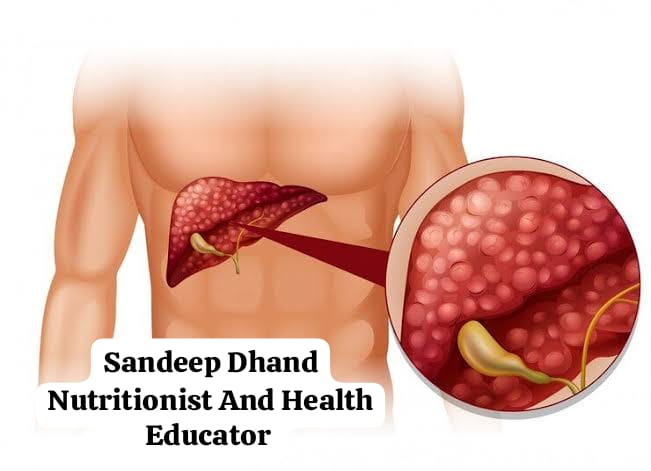
Chronic alcohol use is a major cause of liver diseases, including cirrhosis, which can eventually lead to liver cancer. The liver is crucial for detoxifying alcohol, and overburdening it can lead to irreversible damage.
- Colorectal Cancer
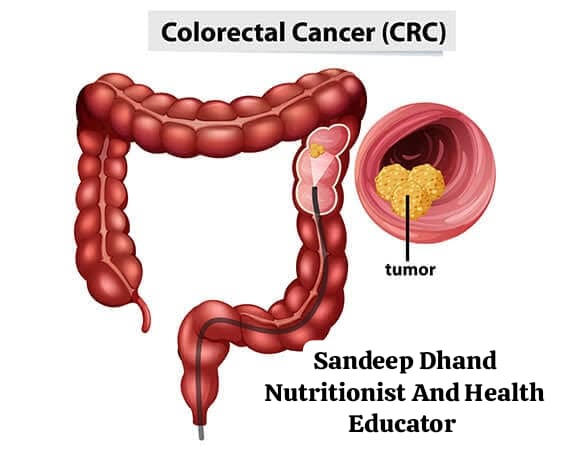
Studies suggest that alcohol consumption can increase the risk of cancers in the colon and rectum. This is thought to be due to the effects of alcohol on gut bacteria and the intestinal lining.
How Much Alcohol is Too Much?
The risk of cancer increases with the amount and frequency of alcohol consumption. While occasional drinking may not pose a significant risk, consistent heavy drinking does.
Moderate Drinking: For most adults, moderate drinking is defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
Heavy Drinking: Consuming more than these limits regularly can lead to serious health risks, including cancer.
Binge Drinking: Drinking a large amount of alcohol in a short period, even occasionally, can also be harmful.
Why Some People are at Higher Risk
Not everyone who drinks alcohol will develop cancer, but certain factors can increase the risk:
- Genetics: Some people have genetic variations that make it harder for their bodies to process alcohol safely, increasing their risk of alcohol-related cancers.
- Smoking: Combining alcohol with smoking amplifies the risk, as both substances damage cells and promote cancer growth.
- Diet: A poor diet lacking essential nutrients can make the body more vulnerable to the harmful effects of alcohol.
- Gender: Women are generally more susceptible to alcohol-related harm than men, partly due to differences in body composition and metabolism.
Can You Reduce the Risk?
Yes, you can reduce the risk of alcohol-related cancers by making healthier lifestyle choices:
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Stick to moderate drinking guidelines or consider abstaining altogether if you are at higher risk.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet to provide your body with the nutrients it needs to repair DNA and fight damage.
- Avoid Smoking: The combination of alcohol and tobacco significantly increases cancer risk, so quitting smoking is crucial.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of cancers linked to obesity and alcohol.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with medical guidelines and consult your doctor about your personal risk factors.
The Role of Awareness
Many people are unaware of the link between alcohol and cancer. Public health campaigns play a vital role in spreading awareness and encouraging people to make informed decisions. The alcohol industry often markets its products without highlighting the potential risks, so it is up to individuals to educate themselves and take precautions.
Conclusion
While alcohol is a part of many cultures and social traditions, its impact on health cannot be ignored. The link between alcohol and cancer is well-documented, and understanding this connection is the first step toward making healthier choices. Limiting alcohol intake, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed can significantly reduce the risks.
Remember, your health is in your hands. Moderation and awareness are key to enjoying life while protecting yourself from preventable diseases like cancer. If you or someone you know is struggling with alcohol consumption, seek professional help and support to make positive changes.