Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
The HbA1c test, also known as the glycated hemoglobin test or A1c test, is a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing and managing diabetes. It provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months by measuring the percentage of hemoglobin proteins in red blood cells that are coated with sugar (glycated). Here’s everything you need to know about this test, its importance, and how it helps diagnose and monitor health conditions.
- What is the HbA1c Test?

HbA1c stands for hemoglobin A1c. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout your body. When glucose (sugar) enters your bloodstream, it binds to hemoglobin. The HbA1c test measures how much glucose is attached to hemoglobin over the average lifespan of red blood cells, which is about 120 days.
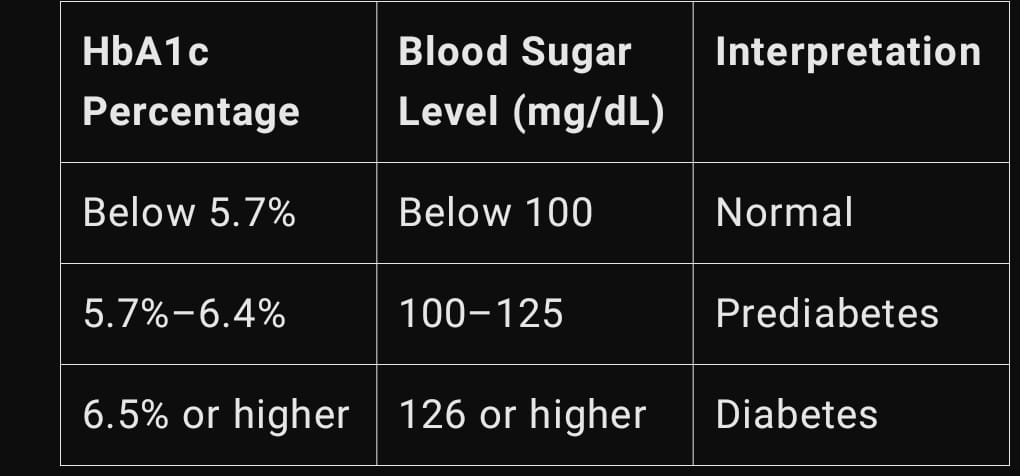
Normal Range: Less than 5.7%
Prediabetes Range: 5.7% to 6.4%
Diabetes Range: 6.5% or higher
The test provides a reliable picture of long-term glucose control, unlike daily blood sugar tests that show short-term fluctuations.
- Why is the HbA1c Test Important?
The HbA1c test is crucial for several reasons:
A. Early Diagnosis of Diabetes
It helps identify undiagnosed diabetes or prediabetes, even in individuals who might not exhibit symptoms. This early detection can prevent the progression of the disease.
B. Monitoring Diabetes
For those already diagnosed, the test is a standard way to monitor how well the blood sugar levels are being controlled over time. It helps guide treatment plans, whether through medication, lifestyle changes, or dietary adjustments.
C. Reducing Complications
Consistently high HbA1c levels are associated with complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular testing ensures timely intervention to mitigate these risks.
- How Does the Test Work?
The HbA1c test is simple and involves drawing a small blood sample from a vein or via a finger prick. The sample is analyzed in a laboratory to determine the percentage of glycated hemoglobin.
Factors Affecting Results
Certain factors can influence HbA1c levels, including:
Anemia or blood loss
Kidney or liver disease
High intake of certain vitamins or medications
Discuss any medical conditions or treatments with your doctor before the test for accurate interpretation.
4. How to Interpret the Results?
Goal for Diabetic Patients
For most people with diabetes, the target HbA1c level is below 7%. However, this can vary based on age, other health conditions, and individual treatment plans.
- Why is it Necessary?
A. Long-Term Glucose Control
Unlike daily blood glucose tests, which can fluctuate due to diet, exercise, or stress, the HbA1c test offers a broader picture of your glucose levels over several months.
B. Identifying Risks
A high HbA1c level indicates poor glucose control, increasing the risk of complications like:
Heart disease
Stroke
Kidney failure
Neuropathy (nerve damage)
Retinopathy (eye damage leading to blindness)
C. Personalizing Treatment
The results help healthcare providers adjust medications, recommend dietary changes, or suggest lifestyle modifications tailored to individual needs.
- Diseases and Conditions Detected
While the primary use of the HbA1c test is in diagnosing and managing diabetes, it can also provide insights into other health conditions:
Prediabetes: Early indication of potential diabetes development
Uncontrolled Diabetes: Alert to poor management or the need for a change in therapy
Hypoglycemia Risks: Too much sugar control can also be harmful
Iron Deficiency Anemia or Hemolytic Disorders: Impact HbA1c accuracy
- How Often Should You Get Tested?
The frequency of the HbA1c test depends on your health status:
No Diabetes: Once every 1-3 years for routine screening
Prediabetes: Annually to monitor progression or reversal
Diabetes: Every 3-6 months to ensure good management
- Can the HbA1c Test Replace Other Blood Sugar Tests?
No, it complements other tests but doesn’t replace them. The HbA1c test provides a long-term view, while daily blood sugar testing gives real-time data that’s crucial for immediate treatment decisions.
- How to Lower HbA1c Levels?
If your HbA1c levels are high, you can lower them with these strategies:
Healthy Diet: Focus on whole grains, vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while avoiding sugary foods.
Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week.
Weight Management: Losing even 5–10% of body weight can significantly lower blood sugar levels.
Medications: Use prescribed drugs consistently. Consult your doctor about insulin or other treatments if necessary.
Stress Management: Stress can elevate blood sugar levels; practices like yoga or meditation can help.
- Limitations of the HbA1c Test
While highly reliable, the test has limitations:
May not be accurate in individuals with:
Hemoglobin variants (e.g., sickle cell anemia)
Recent blood transfusions
Severe anemia
Doesn’t capture short-term glucose fluctuations
Conclusion

The HbA1c test is an essential tool for understanding long-term blood sugar control and preventing complications associated with diabetes. It serves as both a diagnostic and monitoring mechanism, offering insights into your overall health. Ensuring regular testing, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and collaborating with healthcare professionals are key to managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of severe complications.
By recognizing the importance of this test and acting on its results, individuals can take proactive steps toward better health outcomes.
