Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
Introduction
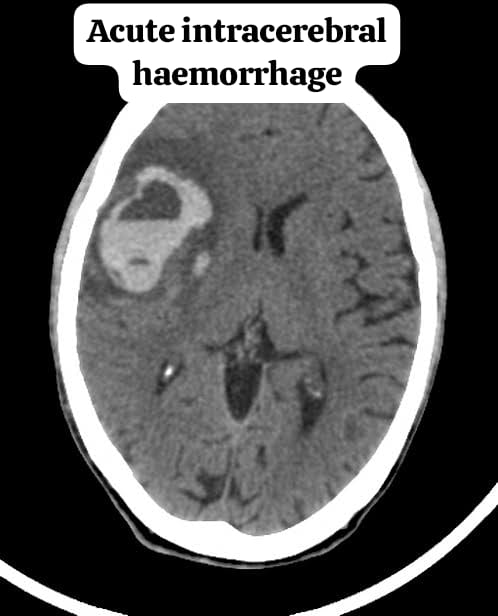
Acute cerebral hemorrhage is a severe medical condition that involves bleeding in the brain. This occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts, leading to the leakage of blood into the surrounding brain tissue. This condition can cause damage to brain cells, increase pressure in the brain, and result in life-threatening complications if not treated promptly.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies for acute cerebral hemorrhage.
Causes of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage
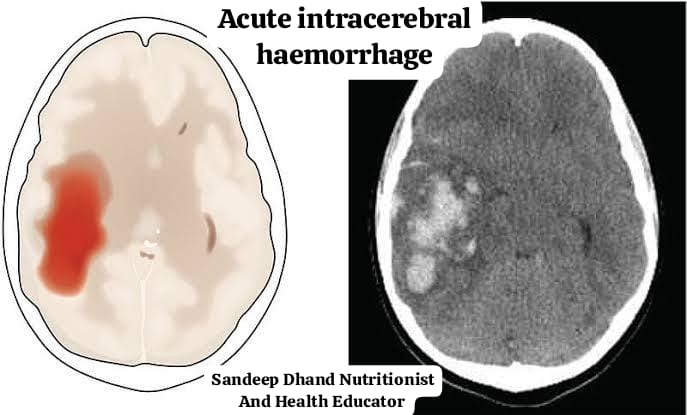
There are several reasons why an acute cerebral hemorrhage can occur. These include:
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension):
Chronic high blood pressure weakens the walls of blood vessels, making them more prone to rupture. - Head Trauma:
Injuries from falls, accidents, or sports can damage blood vessels, leading to bleeding. - Aneurysms:
An aneurysm is a weak spot in a blood vessel that can balloon out and rupture. - Blood Disorders:
Conditions like hemophilia or the use of blood-thinning medications can impair the blood’s ability to clot, increasing the risk of bleeding. - Brain Tumors:
Tumors can press against blood vessels, causing them to burst. - Substance Abuse:
Drugs like cocaine or excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and damage blood vessels. - Vascular Malformations:
Abnormal connections between blood vessels, known as arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), can lead to hemorrhages.
Symptoms of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage
The symptoms of an acute cerebral hemorrhage depend on the location and severity of the bleeding. Common signs include:
- Severe Headache:
Sudden, intense headaches are a hallmark symptom. - Weakness or Numbness:
Usually on one side of the body, such as the arm, leg, or face. - Difficulty Speaking:
Slurred speech or trouble forming sentences. - Vision Problems:
Blurred or double vision may occur. - Loss of Balance:
Trouble walking or a sensation of dizziness. - Confusion:
Difficulty understanding surroundings or remembering events. - Seizures:
Sudden jerking movements or convulsions. - Unconsciousness:
In severe cases, the person may lose consciousness.
Diagnosis of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage
Diagnosing a cerebral hemorrhage requires medical imaging and tests:
- CT Scan:
A CT scan provides detailed images of the brain and can quickly detect bleeding. - MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
An MRI can show more detailed images and is used to locate smaller bleeds. - Angiography:
This test examines blood vessels to identify aneurysms or malformations. - Blood Tests:
These are used to check clotting factors and rule out blood disorders.
Treatment of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage
Immediate medical attention is crucial for treating cerebral hemorrhage. Treatment options include:
- Medications:
Blood pressure-lowering drugs to reduce strain on blood vessels.
Drugs to prevent seizures.
Medications to control swelling in the brain.
- Surgery:
In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the blood and reduce pressure on the brain.
Repairing ruptured blood vessels or clipping an aneurysm.
- Rehabilitation:
After initial treatment, rehabilitation may be necessary to regain lost skills, such as speech therapy or physical therapy.
Prevention of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of a cerebral hemorrhage:
- Manage Blood Pressure:
Regularly monitor and control hypertension with a healthy lifestyle and medications. - Avoid Smoking and Alcohol:
These substances can damage blood vessels over time. - Maintain a Healthy Diet:
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and low in salt can improve vascular health. - Exercise Regularly:
Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces blood pressure. - Protect Your Head:
Wear helmets during risky activities and use seat belts while driving. - Manage Medical Conditions:
Treat diabetes, high cholesterol, and other conditions that can increase the risk of hemorrhage.
Conclusion
Acute cerebral hemorrhage is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting preventive measures can help minimize risks. With timely intervention and proper care, recovery is possible, though rehabilitation may take time.
