Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes cells to build up rapidly on the skin’s surface, forming scales and red patches that can be itchy and sometimes painful. It is an immune system problem that triggers skin cells to multiply much faster than normal. This results in patches of skin that are thick, dry, and flaky. Psoriasis is not contagious, meaning it cannot spread from one person to another through touch or other means.
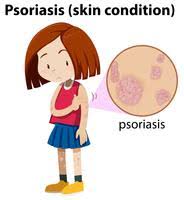
Here’s everything you need to know about this condition in simple terms:
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with its unique characteristics:
- Plaque Psoriasis:
The most common type.
Causes raised, inflamed, and scaly patches on the skin.
Often found on elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- Guttate Psoriasis:
Appears as small, drop-shaped sores on the skin.
Often triggered by bacterial infections like strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis:
Found in skin folds such as under the breasts, around the groin, or near the buttocks.
Causes shiny, red patches of skin.
- Pustular Psoriasis:
Characterized by white pustules (blisters filled with pus) surrounded by inflamed skin.
Can occur on specific areas like the hands and feet or all over the body.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis:
A rare but severe form.
Causes widespread redness, scaling, and shedding of the skin, often accompanied by pain and itching.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis vary depending on the type but commonly include:
Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales.
Dry or cracked skin that may bleed.
Itching, burning, or soreness in the affected areas.
Thickened or ridged nails (nail psoriasis).
Stiff and swollen joints (if psoriasis is associated with arthritis).
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, speeding up the production process.
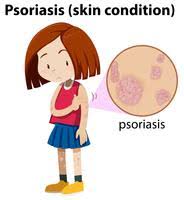
Some common triggers include:
- Infections: Such as strep throat or skin infections.
- Stress: Emotional stress can worsen psoriasis or trigger flare-ups.
- Weather: Cold and dry weather often aggravates symptoms.
- Injuries to the Skin: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburn can trigger psoriasis.
- Medications: Certain drugs like lithium and beta-blockers can cause flare-ups.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen symptoms.
Who Gets Psoriasis?
Anyone can develop psoriasis, but it often begins between the ages of 15 and 35. It can also occur later in life. If one or both parents have psoriasis, the chances of developing the condition increase.
Diagnosis
Doctors typically diagnose psoriasis by examining the skin, scalp, and nails. In some cases, a small skin sample (biopsy) may be taken for further examination to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Although there is no cure for psoriasis, treatments can help control symptoms and improve the quality of life. Treatments include:
- Topical Treatments:
Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and slow cell production.
Vitamin D Analogs: Slow skin cell growth.
Moisturizers: Keep the skin hydrated to reduce dryness and scaling.
- Phototherapy (Light Therapy):
Uses natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light to reduce symptoms.
Effective for moderate to severe psoriasis.
- Systemic Treatments:
Medications like methotrexate, cyclosporine, or biologics that affect the immune system.
Used for severe cases or when other treatments fail.
- Lifestyle Changes:
Regular moisturizing.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques or therapy.
Avoiding triggers like smoking, alcohol, and certain foods.
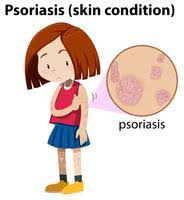
Living with Psoriasis
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but proper care and management can significantly reduce its impact on daily life. Here are some tips:
- Stay Informed: Learn about your condition to manage it better.
- Join Support Groups: Sharing experiences with others who understand can be helpful.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, exercise, and stress management can make a difference.
- Skin Care: Use gentle soaps and avoid harsh scrubbing. Keep the skin moisturized.
- Seek Medical Advice: Consult your doctor regularly to adjust treatments as needed.
Complications
If left untreated, psoriasis can lead to complications such as:
Psoriatic Arthritis: A condition that causes joint pain and stiffness.
Infections: Cracked or open skin increases the risk of infections.
Emotional Impact: Psoriasis can affect self-esteem, leading to anxiety or depression.
Key Takeaways
Psoriasis is a lifelong condition, but with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments, its symptoms can be managed effectively. If you suspect you have psoriasis or are experiencing flare-ups, consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, you’re not alone, and support is available to help you navigate this condition.
