Health Desk
Sandeep Dhand Ludhiana
Journalist & Research Analysist
Introduction
Edema is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the tissues of the body, leading to swelling. It is a common occurrence and can affect various parts of the body, such as the feet, legs, hands, arms, and even internal organs. While edema is often a benign and temporary problem, it can sometimes be a sign of an underlying health condition that requires medical attention. This article will explore the causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for edema in detail.
What is Edema?
Edema refers to the swelling that happens when excess fluid collects in the tissues of the body. The human body maintains a balance of fluid between blood vessels, tissues, and cells. This balance is regulated by a combination of pressure in blood vessels and proteins in the blood that retain fluid. However, when this balance is disrupted, fluid leaks out of the blood vessels and accumulates in the surrounding tissues, resulting in edema.
Causes of Edema
Edema can have numerous causes, ranging from mild to serious. Here are some of the most common reasons for fluid accumulation:
- Injury or Inflammation: When an injury occurs or there is inflammation due to infection, the body’s response is to release chemicals that cause the small blood vessels to leak fluid into the surrounding tissues. This process results in localized swelling, which helps protect the injured area.
- Heart Problems: One of the more serious causes of edema is congestive heart failure. When the heart cannot pump blood effectively, it leads to a backup of fluid, especially in the legs and feet, due to increased pressure in the veins. This condition is known as “peripheral edema.”
- Kidney Disease: The kidneys are responsible for filtering excess fluid and waste from the blood. If the kidneys are not functioning properly, fluid and sodium can accumulate in the body, leading to generalized swelling or “pitting edema.”
- Liver Disease: Cirrhosis or liver damage can result in a decrease in the production of albumin, a protein that helps maintain fluid balance. When the liver fails to produce enough albumin, fluid leaks out of the blood vessels and causes swelling in the abdomen (ascites) and the legs.
- Venous Insufficiency: Chronic venous insufficiency occurs when the veins in the legs are unable to return blood efficiently back to the heart, leading to a buildup of fluid in the tissues. This is a common cause of leg swelling, especially in older adults.
- Medications: Several medications can cause fluid retention and lead to edema. These include corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), calcium channel blockers, and certain medications used for high blood pressure. In such cases, the edema is usually a side effect of the medication.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, a woman’s body retains more water and blood to support the growing baby. Increased pressure on the veins and hormonal changes can also contribute to swelling in the feet and ankles, which is common during pregnancy.
- Lymphatic System Issues: The lymphatic system helps drain excess fluid from tissues. When lymph nodes or lymph vessels are damaged or removed (e.g., after cancer surgery), lymphatic fluid can accumulate in the affected area, causing swelling known as “lymphedema.”
Types of Edema
Edema can be categorized based on the affected area or the underlying cause:
Peripheral Edema: This type affects the legs, ankles, feet, arms, and hands. It is commonly caused by heart failure, venous insufficiency, or prolonged standing or sitting.
Pulmonary Edema: In pulmonary edema, fluid accumulates in the lungs, making it difficult to breathe. This is often caused by congestive heart failure and requires urgent medical attention.
Cerebral Edema: Cerebral edema refers to fluid accumulation in the brain. It can result from head injuries, infections, or strokes, and it is a serious condition that requires immediate treatment.
Macular Edema: This type occurs when fluid builds up in the macula, a part of the retina in the eye. It can cause vision problems and is commonly associated with diabetes.
Lymphedema: This occurs when the lymphatic system is compromised, preventing the drainage of lymphatic fluid. It commonly happens after surgery or radiation treatment for cancer.
Symptoms of Edema
The symptoms of edema can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition:
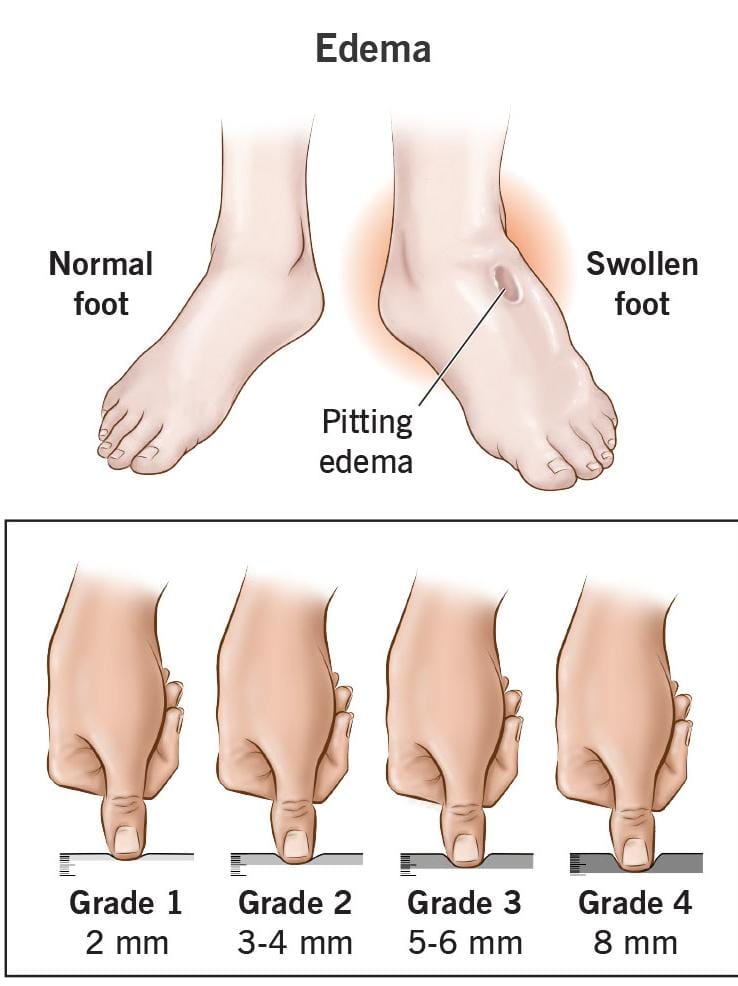
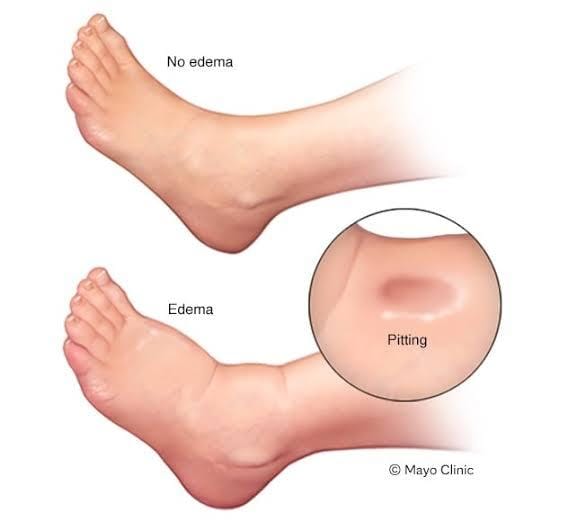
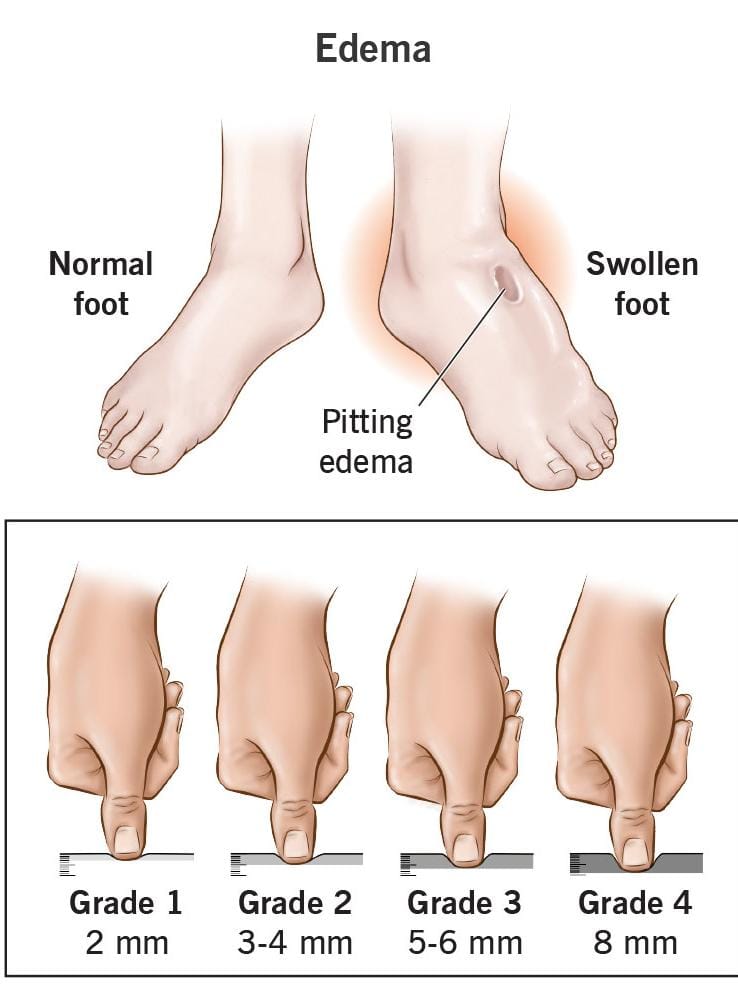
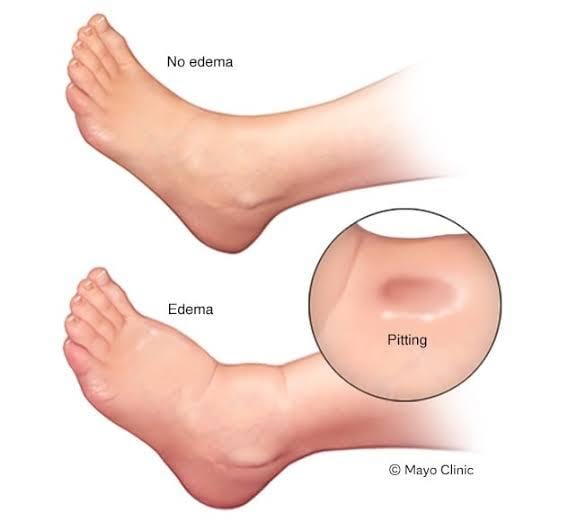
- Swelling: The most noticeable symptom is swelling in the affected area. The skin may appear stretched, shiny, and puffy.
- Pitting: In cases of severe edema, pressing a finger into the swollen area may leave an indentation, which is known as “pitting edema.”
- Stiffness and Discomfort: Edema can cause the affected area to feel heavy, tight, or stiff, making movement difficult.
- Shortness of Breath: If the lungs are affected (as in pulmonary edema), shortness of breath, especially while lying down, can occur. This requires immediate medical attention.
- Weight Gain: Edema can cause an unexplained increase in body weight due to fluid retention.
Diagnosis of Edema
The diagnosis of edema involves a physical examination and an evaluation of medical history. The healthcare provider may also perform specific tests to determine the underlying cause of edema:
- Blood Tests: To check for kidney, liver, and heart function as well as electrolyte levels.
- Urine Tests: To assess kidney function and look for protein levels that could indicate kidney disease.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs may be used to visualize internal organs and identify the cause of fluid accumulation.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To evaluate heart function and detect any abnormalities in the heart’s rhythm.
Treatment of Edema
The treatment for edema focuses on addressing the underlying cause and reducing the swelling:
- Lifestyle Changes:
Elevate the Affected Area: Keeping the swollen limb elevated above heart level can help reduce swelling.
Compression Garments: Wearing compression stockings or sleeves can improve blood circulation and reduce fluid buildup in the limbs.
Limit Salt Intake: Reducing dietary sodium can help prevent fluid retention and decrease the severity of edema.
- Medications:
Diuretics: Commonly known as “water pills,” diuretics help the kidneys excrete excess fluid and sodium. They are often used in cases of heart failure or kidney disease.
Heart Medications: If edema is due to heart failure, medications that improve heart function may also be prescribed.
- Treating Underlying Conditions:
If the edema is due to a specific condition like kidney disease, heart failure, or liver disease, treatment of that condition is necessary to manage the edema.
- Exercise:
Physical activity can help improve circulation and prevent fluid buildup, especially in the lower extremities.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
Taking breaks to move around can help prevent fluid accumulation in the legs and feet.
Complications of Edema
If untreated, edema can lead to complications, including:
Skin Ulcers: Prolonged swelling can cause skin to stretch and break down, resulting in sores or ulcers, particularly in the legs.
Increased Risk of Infection: Swollen tissues are more prone to infection, especially cellulitis.
Decreased Mobility: Severe swelling can make it difficult to move the affected limb, leading to reduced mobility and increased stiffness.
Conclusion
Edema is a common medical condition that involves the accumulation of excess fluid in the body’s tissues, resulting in swelling. While it is often temporary and not serious, it can also indicate a potentially dangerous underlying health issue. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and appropriate treatments is crucial for managing this condition effectively. If you experience persistent or severe edema, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
